PCOS and Clomid Fertility Treatment and Pregnancy
PCOS and ovulation problems and Clomid treatment
Clomid (clomiphene citrate or Serophene) is an oral medication that is commonly used for the treatment of infertility.
- It is often given to try to induce ovulation in women that do not develop and release an egg (ovulate) on their own
- Women who do not ovulate (without drugs) are said to have a condition called anovulation
- The most common cause of anovulation is polycystic ovarian syndrome, PCOS
- This page is about Clomid treatment for women with polycystic ovarian syndrome, or with irregular menstrual cycles
- Clomid for women with regular periods is discussed elsewhere
|
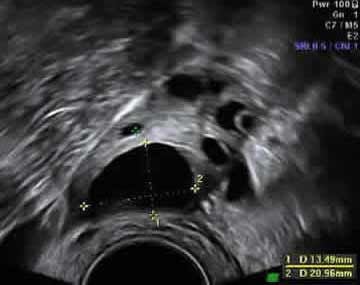
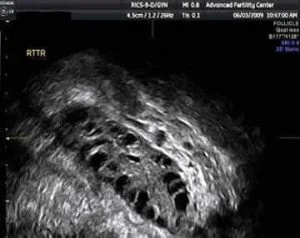
Ultrasound picture of a polycystic ovary Many small, immature follicles (black circles) are seen |
Ultrasound picture of a polycystic ovary Many small, immature follicles (black circles) are seen |
Ready for an Appointment in the Chicago Area?
If you’re ready to explore treatment, contact the award-winning team at AFCC.
Find a Prelude Fertility Clinic Location Near You
The Prelude Network is the fastest-growing network of fertility centers in North America.
PCOS and Clomid Treatment – Ovulation and Pregnancy Success Rates
-
The chance for pregnancy with fertility treatments for PCOS is very good. The great majority of women with polycystic ovarian syndrome will be able to have a baby with treatment.
- For women under age 35, the question is more about which PCOS treatment will work – and not so much about whether any treatment will work.
Ovulation Success Rates Women with PCOS will often ovulate after taking Clomid. However, this is variable and some will not respond to Clomid at all
- About three fourths of women that are not ovulating will ovulate on Clomid at some dosing level.
- Women under 35 with PCOS should have about a 15% chance for pregnancy per month with Clomid treatment (for about 3-4 months) – if they ovulate with Clomid (if sperm and fallopian tubes are normal).
Clomid for PCOS – Pregnancy Success Rates
- Only about 50% of women that ovulate with Clomid get pregnant with it
- For women with PCOS under age 35 in our in vitro fertilization program the success rate is about 70% for pregnancy with one IVF cycle, and about 60% for live birth (miscarriages account for the different rates).
- See our IVF Success Rate Statistics
-
- Day one is counted as the first day of menstrual bleeding.
- The period can be from a spontaneous menstrual period or from a period induced with a progestin medication such as Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate).
Inducing a Period (if needed)
- In order to induce a period, Provera is given for 5 to 10 days at a dose of 5 or 10mg daily.
- The period usually starts within 2-7 days after the last Provera pill is taken.
Starting Clomid
- Clomid is started early in the menstrual cycle and is taken for five days either from cycle days 3 through 7, or from day 5 through 9.
- Clomid is usually started at a dose of one tablet (50mg) daily – taken any time of day.
Increasing Clomid Dosage (if needed)
- If the patient does not ovulate on the starting dose, Provera is often given to induce a period – then a 100mg dose of Clomid is tried.
- If she does not ovulate on a 100 mg dose, then 150mg is sometimes tried.
Clomid Dosing Recommendations
Clomid works best when the lowest dose that results in ovulation is used:
- If a woman ovulates on 50mg then increasing to 100mg is probably of no benefit – and may result in increased side effects.
- Many women will ovulate on 50 or 100mg, and some will require 150 mg in order to get an ovulatory response.
- Some pregnancies will occur on clomiphene doses above 100mg. However, increasing the Clomid dose to 200mg results in very few additional pregnancies.
-
For women that do not ovulate on their own, the average day that ovulation occurs is about 8 to 10 days after completing a 5 day course of Clomid.
- That means that a woman taking Clomid on days 5-9 will often ovulate on about day 16-20 of the cycle.
- However, there is significant variation in how long it takes ovulate using Clomid. Some will ovulate much later – as late as two or three weeks after the last clomiphene tablet.
-
There is no set number of cycles of Clomid that should be done before moving on to other fertility treatments. Several variables are involved in the decision about moving on to more aggressive therapy. No Ovulation Results After increasing Clomid Dosage
- If a woman is not ovulating on a low dose of Clomid, the dose should be increased
- If not ovulating at 150 mg then other therapies should be attempted
Female age and Clomid treatment and when to be more aggressive Relatively fewer cycles should be done with an older female partner Clomid probably should not be used at all if the female age is 40 or older because of the significantly reduced fertility potential Women 38 or older should probably start fertility treatment with a fertility specialist – rather than with their gynecologist If the female is under 38 years old and the sperm is good then usually 3-6 months of Clomid cycles (with good ovulation) are often tried Personal factors regarding Clomid treatment and when to be more aggressive The patient’s own sense of urgency Other personal factors, including degree of severity of any Clomid side effects Financial considerations.
Clomid and Treatment Costs
Clomid is not expensive and costs between about $10 and $100 per cycle depending on the dose and whether a brand name or generic clomiphene citrate is used.
- The average cost for the Clomid pills for a cycle is about $40
- The average cost for generic clomiphene citrate is about $15
- Approximate average costs in the US (and our fees) for various fertility treatments