Early Pregnancy – HCG Levels and Ultrasound Findings
When pregnancy begins depends on how “pregnancy” is defined. Does it begin when the sperm first penetrates the egg? Does it begin when the male and female pronuclei (see picture below) containing the chromosomal material move close together and decondense in the newly fertilized egg?
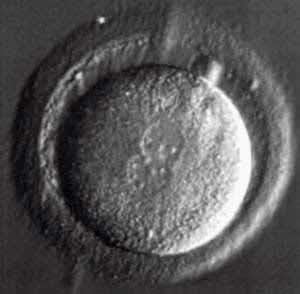
One cell human embryo from IVFHuman zygote embryo several hours after fertilization 2 circular structures (pronuclei) in the center contain maternal and paternal DNA Sperm and egg were put together 16 hours ago
Does pregnancy begin when the male and female chromosomes pair up with each other and the fertilized egg subsequently divides into a 2-cell embryo? Does it begin when the embryo implantation begins about 6 to 8 days after ovulation? Or, does it begin when the woman recognizes that she is pregnant after her missed menstrual period and positive pregnancy test?
Understanding HCG Levels in Pregnancy
HCG, or human chorionic gonadotropin, is a hormone made by the pregnancy that can be detected in the mother’s blood or urine even before the woman’s missed period. This hormone is what we look for with a pregnancy test.
HCG is first detectable in the blood as early as 7-8 days after ovulation by very sensitive HCG assays (research assays); however, most blood pregnancy tests detect HCG levels about 10-11 days after. During early pregnancy, HCG levels double every two to three days; about 85% of normal pregnancies have double HCG levels every 72 hours. HCG levels peak at about 8-10 weeks of pregnancy and then decline, remaining at lower levels for the rest of the pregnancy.
During early pregnancy, it’s important to exercise caution in placing excessive emphasis on HCG levels, as there is a large variation in a “normal” HCG level for any given time in pregnancy. For example, miscarriages and ectopic (tubal) pregnancies tend to show lower HCG levels eventually, but often have normal levels initially. Some normal pregnancies will have quite low levels of HCG – and deliver perfect babies.
Ready for an Appointment in the Chicago Area?
If you’re ready to explore treatment, contact the award-winning team at AFCC.
Find a Prelude Fertility Clinic Location Near You
The Prelude Network is the fastest-growing network of fertility centers in North America.
Ultrasound Findings
For women who have had an HCG injection as part of their fertility treatment, the hormone takes about 5-14 days to clear from her system, depending on the dose and the individual woman. This can cause problems with the interpretation of pregnancy tests done earlier than 14 days after an HCG injection. Ultrasound findings after 5-6 weeks of pregnancy are much more predictive of pregnancy outcome than are HCG levels.
Ultrasound findings are preferred for a multitude of reasons, including:
- Direct visualization of the pregnancy
- The ability to accurately estimate the gestational age of the pregnancy
- Assessing pregnancy viability
- Confirming the location of the pregnancy
- Detecting multiples (twins, triplets, etc.)
While HCG levels are useful in early pregnancy to confirm that a pregnancy is progressing, they have limitations. HCG levels can vary widely among individuals and do not provide information about the location, viability, or detailed development of the pregnancy. Therefore, while HCG levels can indicate the presence of a pregnancy, ultrasound is the more comprehensive and reliable method for predicting and monitoring pregnancy.