Ovarian Stimulation IVF Protocols Medications and Drugs for In Vitro Fertilization
- In order to maximize success rates with in vitro fertilization we want a good number of high quality eggs from the woman. We generally try to get about 10-18 eggs at the egg retrieval procedure.
- IVF success rates correlate with the number of eggs retrieved.
- There are several ovarian stimulation medication protocols that are used to “pump up” the ovaries to make enough follicles and eggs. Without stimulating medications, the ovaries make and release only 1 mature egg per menstrual cycle (month).
The commonly used stimulation regimens include injections of follicle stimulating hormone – FSH.
There are 3 very commonly used ovarian stimulation protocols for in vitro fertilization:
- Luteal Lupron protocol also called “long Lupron”, or agonist “down regulation”
- Antagonist protocols that involve use of of the GnRH antagonist medications
- Flare and micro-flare protocols, also called short Lupron protocols, or short protocols are used for patients expected to have a low response to ovarian stimulation
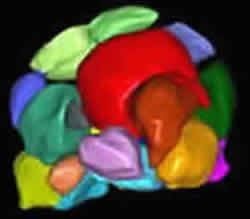
Follicles in 3D ultrasound view from stimulated ovary
3D ultrasound picture of multiple follicles in an ovary stimulated for IVF
Our 3D ultrasound machines calculates accurate follicle sizes
IVF stimulation protocols in the US generally involve the use of 3 types of drugs:
- A medication to suppress the LH surge and ovulation until the developing eggs are ready.
There are 2 classes of drug used for this:- GnRH-agonist (gonadotropin releasing hormone agonist) such as Lupron
- GnRH-antagonist such as Ganirelix or Cetrotide
- FSH product (follicle stimulating hormone) to stimulate development of multiple eggs
- Gonal-F, Follistim, Bravelle, Menopur
- HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) to cause final maturation of the eggs
The ovaries are stimulated with the injectable FSH medications for about 7-12 days until multiple mature size follicles have developed.
What is the goal of a good in vitro fertilization ovarian stimulation?
With ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization, the goal is to get approximately 8 to 15 quality eggs at the egg retrieval procedure.
We do not want to have overstimulation of the ovaries which can lead to significant discomfort for the woman and in rare cases can result in ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, OHSS.
In recent years we have used a Lupron trigger to reduce or eliminate risks for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome. Our 2014 study on using Lupron triggers to maintain high success rates and reduce any risks for hyperstimulation. We also do not want the ovarian stimulation to be insufficient and only give us a few eggs if we might have been able to obtain more by using higher medication doses, etc.
In vitro fertilization can be successful with a very low number of eggs retrieved, but success rates are substantially higher when more eggs are recovered.
With the ovarian stimulation, the job of the infertility specialist doctor is to:
- Select a proper medication protocol and dosing regimen
- Monitor the patient’s stimulation progress so that medication doses can be adjusted properly
- Trigger with hCG at the ideal time. Triggering to early or too late reduces success and can sometimes increase the risk for ovarian hyperstimulation (if triggered late).
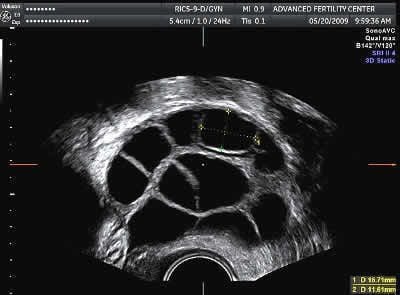
Stimulated ovary for ivf
Ultrasound of multiple follicles (black areas) in a stimulated ovary
Yellow cursors outline a 15 mm diameter follicle
Most mature sized follicles (about 15-20 mm diameter) will give mature eggs at retrieval
Using the latest 3D ultrasound technology to obtain precise measurements
Quality control throughout the entire process is very important with in vitro fertilization. One of the ways that we have improved quality control in our program is by using highly specialized ultrasound equipment.
We use a GE Voluson E8 ultrasound machine with a computer built-in that can outline and accurately measure the developing follicles.
We have found that this method is more precise and reliable as compared to the traditional method – which is usually manual measurements in two dimensions.
The computer in the machine traces the follicle borders (in three dimensions). It then calculates a volume for each one. From the volume it calculates an average diameter for each follicle (as if it was a sphere).
This technology gives us more accurate and reliable measurements than we had in the past.
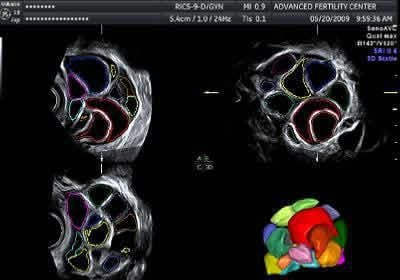
2D and 3D ultrasound pictures with all 3 planes in stimulated ovary
Ultrasound picture shows the three planes in a volume of data from one ovary
This patient is near the end of the stimulation – numerous follicles seen in the ovary
Upper left = sagittal plane, upper right = transverse plane, lower left = coronal plane
At lower right is a 3-D view of the follicles (generated by the computer)
See below for close up views of the same images
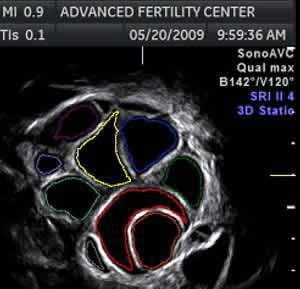
Close-up view of the transverse plane (from the same image above)
Computer generated tracings of follicles are different colors
Rendered 3D ultrasound picture of follicles in stimulated ovary
Close-up of a 3D view of multiple follicles in a stimulated ovary
A computer in the machine made the “rendered” image from a captured volume of data
It is obvious that follicles are not spherical in shape
How is the monitoring of the in vitro fertilization stimulation done?
- We try to stimulate the woman to get at least 4 follicles with sizes of 14-20mm diameter.
- Ideally, there would be at least 8 follicles between 13-20 mm.
- The goal is to get a good number (about 8-15) of quality eggs
- Blood hormone levels and developing follicle sizes are monitored.
- Ultrasound is used to measure the follicles (discussed above on this page)
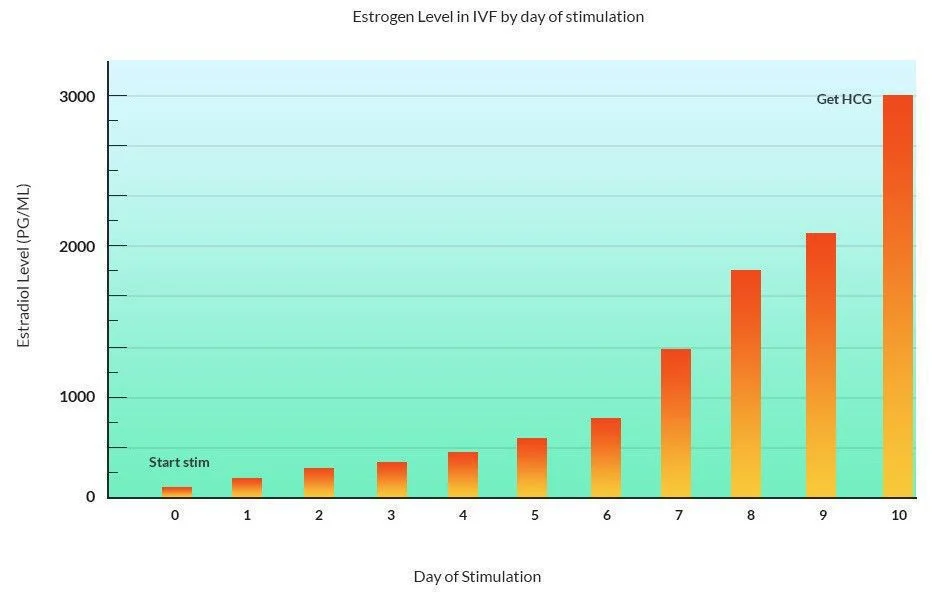
- Estrogen hormone blood levels are important. Estrogen (actually estradiol) levels are usually under 60 pg/ml at cycle baseline and rise significantly as multiple follicles develop.
- Peak estradiol levels in IVF at the time of HCG are usually between 1000 and 4000 pg/ml.
- The stimulating process usually takes about 8-10 days
Estrogen hormone levels in IVF cycle
Graph showing estrogen hormone levels during an IVF stimulation
Estradiol starts low and rises to 1000 to 4000 pg/ml by the time of the HCG injection
- The HCG injection is given when the estrogen level and the follicle measurements look best for successful outcome. The HCG shot is needed to induce final egg maturation.
- The egg retrieval is planned for 34-35 hours after HCG injection – shortly before the woman’s body might start to release the eggs (ovulate).
How many follicles do you need in order to get pregnant with IVF?
Usually, it is not difficult to get enough follicles to develop. However, sometimes the response of the ovaries is poor – and a low number of growing follicles are seen. The ability of the ovaries to stimulate well and give us numerous eggs can be predicted fairly well by an ultrasound test – the antral follicle count.
The minimum number of follicles needed to proceed with in vitro fertilization treatment depends on several factors, including their sizes, age of the woman, results of previous stimulations and the willingness of the couple (and the doctor) to proceed with egg retrieval when there will be a low number of eggs obtained.
In our experience, IVF success rates are very low with less than 3 mature follicles.
Some doctors will say that you should have at least 5 that measure 14mm or greater while others might do the egg retrieval with only one follicle. Most IVF programs in the US want a minimum of about 3-4 mature (or close to mature) follicles.
Women that are more likely to be low responders to ovarian stimulation would be those that have low antral counts, those women who are older than about 37, women with elevated FSH levels, and women with other signs of reduced ovarian reserve.