Understanding Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS): What Fertility Patients Should Know
Ovarian Hyperstimulation Syndrome (OHSS) is a potentially serious complication from medications used during fertility treatments, especially in in vitro fertilization (IVF). While most cases of OHSS resolve without intervention, it's important for patients to understand the symptoms, risk factors, and prevention strategies to deal with OHSS and report appropriate symptoms to their healthcare providers.
What Is OHSS?
OHSS happens when the ovaries become swollen and fluid leaks into the abdominal cavity due to increased vascular leakiness. This fluid shift is triggered by elevated levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), often in response to human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) use during fertility treatment, and high levels of estrogen from stimulated follicles.
There are two types of OHSS:
-
Early-onset OHSS: Occurs within 4–7 days after the hCG trigger.
-
Late-onset OHSS: Develops 9+ days after the trigger, often due to rising hCG levels from early pregnancy.
Common Symptoms of OHSS
Symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include:
-
Abdominal bloating and pain
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Shortness of breath
-
Rapid weight gain
-
Decreased urine output
-
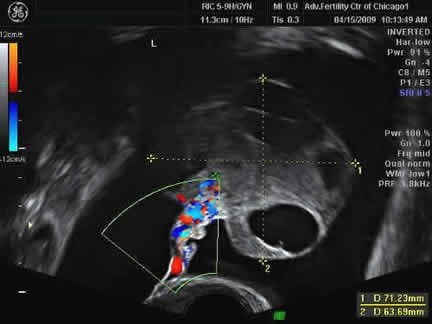
Enlarged ovaries and fluid buildup visible on ultrasound
-
Leg pain or swelling
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your fertility clinic immediately.
Ultrasound showing hyperstimulated ovary and free fluid in the abdomen
Who Is at Risk?
While OHSS can affect anyone undergoing ovarian stimulation, certain patients are more susceptible due to their body’s response to fertility medications. These include:
1. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
Patients with PCOS often have a high number of small follicles and are highly sensitive to gonadotropin stimulation. This can lead to an exaggerated ovarian response, increasing the risk of OHSS.
2. High Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) Levels
AMH is a marker of ovarian reserve (egg supply). High AMH levels typically indicate a large pool of follicles, which can result in excessive follicular development and elevated estrogen levels during stimulation—both of which contribute to OHSS risk.
3. High Antral Follicle Count (AFC)
A high AFC means the ovaries have many recruitable follicles. When stimulated, these follicles can grow rapidly and in large numbers, increasing the chance of fluid leakage and OHSS.
4. Elevated Estradiol Levels During Stimulation
High estradiol levels are a sign of multiple growing follicles. When estradiol rises too quickly or reaches very high levels, it can signal an increased risk of OHSS due to heightened vascular permeability.
5. Young Age and Low Body Weight
Younger patients and those with lower body mass may metabolize fertility medications differently, sometimes leading to a stronger ovarian response and higher OHSS risk.
How Is OHSS Managed?
-
Mild to moderate OHSS: Managed with hydration and monitoring at home or in the clinic.
-
Severe OHSS: May require blood tests, ultrasounds, procedures like paracentesis to drain excess fluid, and rarely, hospitalization.
Prevention Strategies
1. Using a GnRH Agonist (Lupron) Trigger
Instead of hCG, a Lupron trigger induces ovulation with a lower risk of OHSS by avoiding the prolonged stimulation of VEGF.
2. Individualized Dosing of Gonadotropins
Carefully tailored medication protocols based on ovarian reserve testing help prevent overstimulation.
3. Freeze-All Cycles
In high-risk cases, embryos are frozen and transferred in a later cycle to allow OHSS symptoms to resolve before pregnancy hormones can worsen them.
4. Cabergoline Therapy
Cabergoline, a dopamine agonist that reduces the activity of VEGF, may be prescribed to help minimize fluid leakage from blood vessels and reduce the risk of OHSS.
5. Coasting
Coasting is a technique where FSH injections are paused for 1–3 days while monitoring estradiol levels and follicle growth. This allows hormone levels to stabilize before administering the trigger shot, reducing the risk of OHSS. It’s typically used when estradiol levels rise too quickly or reach dangerously high levels.
Why OHSS Awareness Matters
While OHSS is relatively rare—occurring in about 1–5% of IVF cycles—it can be serious. Educating patients about symptoms and prevention helps reduce anxiety and ensures timely care if symptoms arise.
At AFCC, we’re committed to providing personalized fertility care that prioritizes your health and safety. If you have questions about OHSS or your treatment plan, don’t hesitate to reach out to your care team.
Ready to Take the Next Step?
If you're considering fertility treatment and want to learn more about your options—including how we minimize risks like OHSS—schedule a consultation with one of our experienced fertility specialists at Advanced Fertility Center of Chicago. We're here to guide you with personalized care every step of the way.
Categories
About the AFCC Blog
Welcome to the Advanced Fertility Center of Chicago’s blog! Here, you will find information on the latest advancements in fertility care and treatments, including IVF, IUI, third-party reproduction, LGBTQ+ family building, preimplantation genetic testing, and more. Since 1997, we’ve used our experience and continuous investment in the latest fertility technology to help thousands of patients grow their families. Contact us today for more information or to schedule a new patient appointment.