Lupron Down-Regulation Ovarian Stimulation Protocol for IVF
Also called "Long Lupron" or "Luteal Lupron"
Ovarian stimulation protocols for in vitro fertilization using Lupron (leuprolide acetate) or GnRH-agonist drugs.
There are 2 basic ways that we use the GnRH-agonist medications such as Lupron in conjunction with the FSH product in IVF stimulation protocols:
- "Long protocols", also called "luteal Lupron", or "down regulation" protocols
- "Flare" protocols, also called "short" protocols, or "microflare"
Read an overview about ovarian stimulation for in vitro fertilization
Long protocols - also called "down regulation" or "mid-luteal Lupron" protocols
- The "long protocol" used to be the most commonly used IVF protocol in the US. Now the antagonist (Ganirelix) protocols are used more.
- Success rates are the same with less injections and lower risk for ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome if we use an antagonist protocol instead of Lupron down-regulation.
- With this Lupron protocol, the Lupron starts about 7 days before the next expected period - called "mid-luteal" timing.
- The FSH drug is usually started within the first 2-7 days after the period begins.
- The leuprolide acetate dose is often reduced when the FSH product is started.
- The dose and brand name for the FSH product (e.g. Follistim, Gonal-F, Menopur) varies according to the preferences of the physician and the patient's situation.
- Most women get a starting dose between 150 and 375 units of FSH product per day.
- The dose is adjusted as the stimulation progresses.
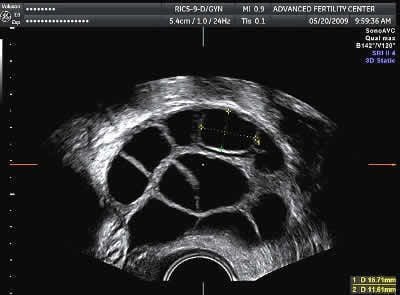
Ultrasound of multiple follicles (black circles) in a stimulated ovary
Yellow cursors outline a 15 mm follicle
How is the monitoring of IVF stimulation done?
- We try to stimulate the woman to get at least 3 or 4 follicles with sizes of 14-20mm diameter. Ideally, there would be about 8 follicles in this range. We want more eggs because the number of eggs we get correlates with success rates.
- Blood hormone levels and developing follicle sizes are monitored.
- Ultrasound is used to measure the follicles
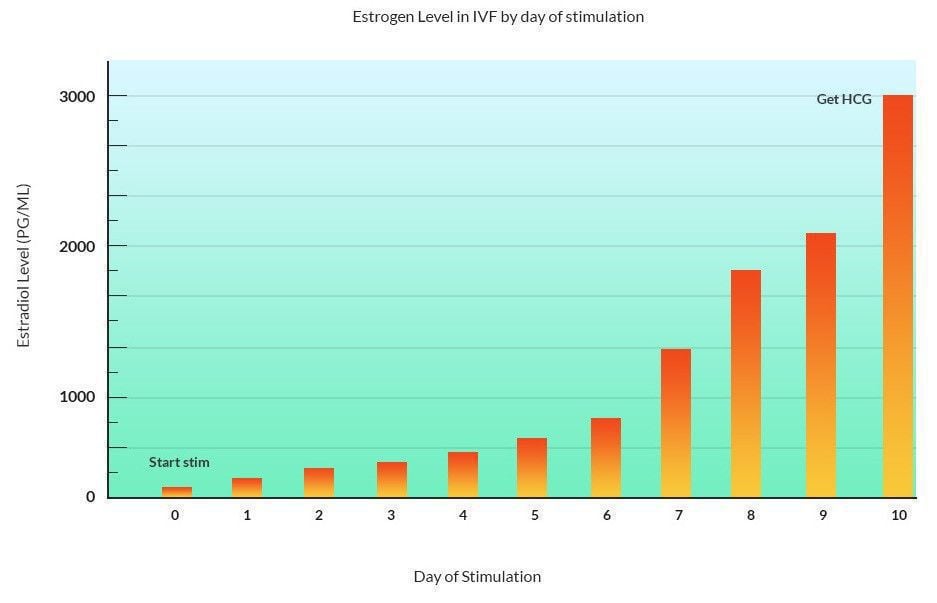
- Estrogen hormone blood levels are important. Estrogen (actually estradiol) levels are usually under 60 pg/ml at cycle baseline and rise significantly as multiple follicles develop.
- Peak estradiol levels on the day of the HCG shot are usually 1000 to 4000 pg/ml.
- The stimulating process usually takes 8-10 days
Graph showing estrogen hormone levels during an IVF stimulation
Estradiol starts low and rises to 1000 to 4000 pg/ml by the time of the HCG injection
- The HCG shot is needed to induce final egg maturation. It is given when the estrogen level and the follicle measurements look best for successful IVF outcome.
- The egg retrieval procedure is planned for 34-36 hours after HCG injection - shortly before the woman's body might release the eggs (ovulate).
What if this stimulation protocol does not work well?
Some women do not respond well to the long protocol using leuprolide. They do not make enough follicles to give a good chance for pregnancy from IVF with this regimen.
- The ability of the ovary to stimulate and develop enough follicles can be predicted by an ultrasound test - antral follicle count
- The AMH blood test and the day 3 FSH blood tests of ovarian reserve can also help to predict response to the IVF drugs
Stop Lupron Protocol
Some women will be "over-suppressed" by the standard long protocol, or are low responders for some other reason. A "stop Lupron" protocol is one possibility for better response to stimulation.
With this protocol, the leuprolide is started at the same time in the cycle, but usually at a lower dose, often at 5 units daily instead of 10 units. It is then stopped completely after the woman gets her period and the FSH product is started.
The LH suppressing ability of this protocol is not as complete as with a standard long protocol. However, the risk for a premature LH surge is still low, and blood tests can be done during the cycle to watch for any LH hormone spikes.
Antagonist stimulation or a microflare protocol are options for IVF stimulation other than the long protocol.
Categories
About the AFCC Blog
Welcome to the Advanced Fertility Center of Chicago’s blog! Here, you will find information on the latest advancements in fertility care and treatments, including IVF, IUI, third-party reproduction, LGBTQ+ family building, preimplantation genetic testing, and more. Since 1997, we’ve used our experience and continuous investment in the latest fertility technology to help thousands of patients grow their families. Contact us today for more information or to schedule a new patient appointment.